Hemorrhoids
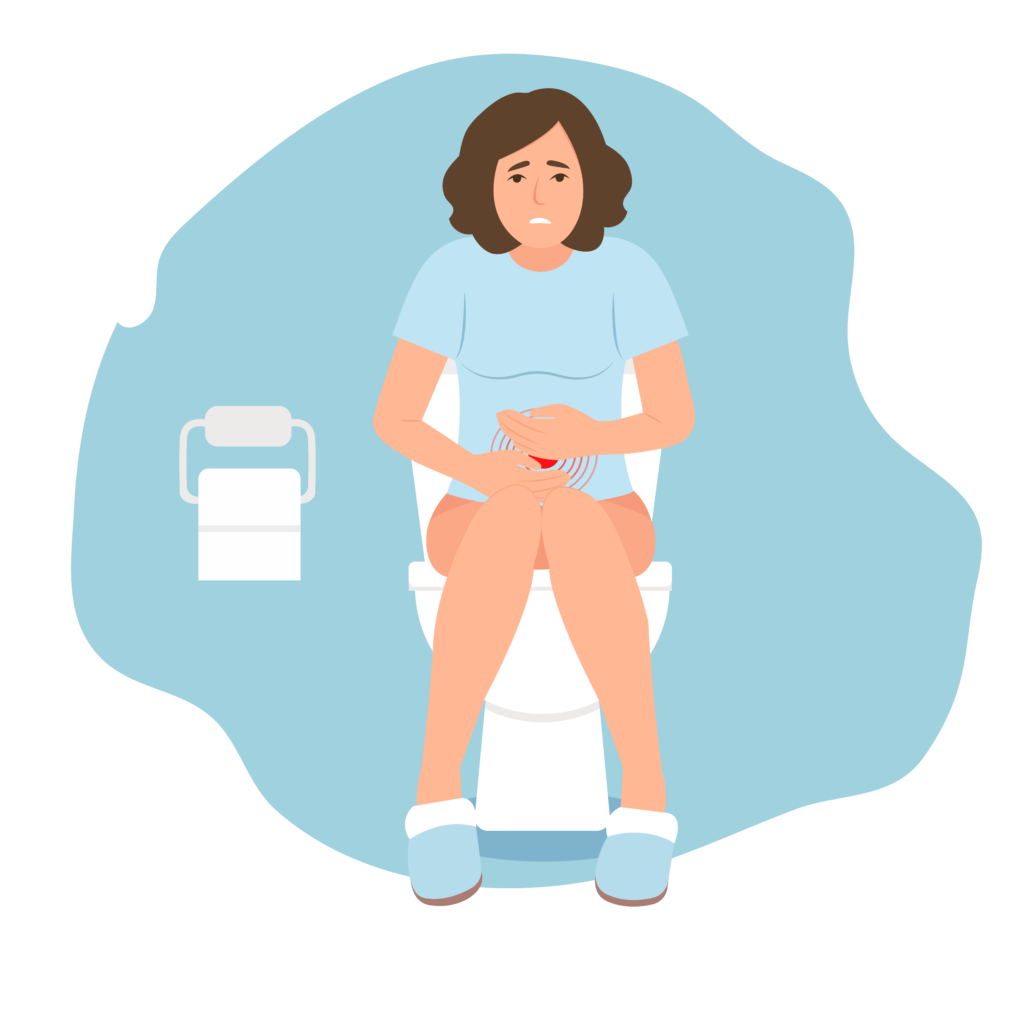



What is hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids, also known as Piles, is a common anorectal condition where – there are swollen veins in the lower part of the rectum, which are affecting millions of people, both men and women at any age around the world, and represent a major medical and socioeconomic problem, where-in symptomatic enlargement and distal displacement of the normal anal cushions is observed.
What are the causes of hemorrhoids / piles?
Various causes of hemorrhoids / piles are as follows:- Chronic constipation
- Chronic diarrhea
- Lifting heavy weights
- Pregnancy
- Straining when passing a stool
- Genetics
Signs & Symptoms
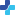
Internal hemorrhoids signs and symptoms include:
Usually painless - not richly supplied by nerves (above dentate line)
Bleeding (splash in pan)
Prolapse
Perianal itching & irritation – due to mucoid discharge

External hemorrhoids signs and symptoms include:
Pain or discomfort- area is richly supplied by nerves
Itching or irritation in the anal region
Swelling around the anus
Bleeding
What are the complications that hemorrhoids / piles will lead to?
Hemorrhoids piles complications include:
Anal Fissures: Straining during bowel movements due to Hemorrhoids / piles can lead to small tears in the lining of the anus.
Strangulation: Internal hemorrhoids have the potential to prolapse and may get trapped outside the anal opening causing cut off of blood supply, which is an emergency condition.
Anemia: Iron-deficiency may eventually result from chronic bleeding of Hemorrhoids.
How to diagnose hemorrhoids / piles?
- Your healthcare provider will examine you, ask about your symptoms and evaluate you.
- External hemorrhoids / piles can be diagnosed by checking the area around the anus.
- To diagnose internal hemorrhoids / piles, your doctor will perform a digital rectal examination. During this, your doctor inserts a gloved and lubricated finger into your rectum and may perform procedures like anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, or colonoscopy to look inside the anus and the rectum. Each of these tests involves using a small camera to diagnose any abnormalities in your anus, rectum, or colon.
- An anoscopy examines the inside of the anus, a sigmoidoscopy examines the last 2 feet of the colon, and a colonoscopy explores the entire colon.
How to treat hemorrhoids / piles?
Conservative Management of hemorrhoids / piles:
-
Sitz bath: - Soak the anal area in warm water for 10 to 15 minutes, at-least two or three times a day.
-
Eating plenty of fibre (for example, fruit, vegetables, cereals, wholegrain bread, oats etc.)
-
Drink lots of fluid, except alcohol and caffeine should be avoided.
-
Avoid medicines that cause constipation.
-
Go to the toilet as soon as possible after feeling the need to defecate.
-
Do not strain on the toilet.
-
Regular exercise.
Medical Management of hemorrhoids / piles:
Several medicinal options are available along with conservative measures like:
-
Medications include painkillers, ointments, creams, and pads, and can help soothe redness and swelling around the anus.
-
Flavonoids: Help to reduce the symptoms of piles like bleeding, pain, swelling, itching and irritation.
-
Corticosteroids: These can reduce inflammation and pain.
-
Laxatives: Laxatives may be used if a person with piles suffers from constipation, which will help to pass the stools more easily with reduced pressure on the lower colon.
Surgical Management of hemorrhoids / piles:
When all the other managements fail to control piles or hemorrhoids then various surgical options are available which your doctor might suggest depending on the type and severity of hemorrhoids / piles:
-
Rubber band ligation: - Is a procedure in which the hemorrhoids is tied off at its base with rubber bands, cutting off the blood flow to the piles, i.e. hemorrhoids. After a few days, the hemorrhoids falls off.
-
Sclerotherapy: Involves an injection of a solution (generally a salt solution) directly into the vein causing piles i.e. hemorrhoids to collapse and shrink. This is effective for grade II and III hemorrhoids.
-
Infrared coagulation: Infrared light coagulation is a device i.e. used as a heat source to quickly coagulate, or clot, vessels supplying blood to the hemorrhoids
-
Hemorrhoidectomy: In grade III & IV the hemorrhoidal tissue that is prolapsed and causing bleeding is surgically removed by various ways under anaesthesia.
-
Stapled Hemorrhoidectomy: Hemorrhoidal tissue is lifted into a ring of tissues with sutures and a stapler removes the hemorrhoids, effectively cutting off blood flow to the tissue



How to prevent hemorrhoids / piles?

General measures to prevent constipation:
Go to the bathroom when you need to go.
Don’t turn the bathroom into a reading room.
Re-assess your diet
Exercise

Drink more water.
Avoid long periods of sitting.

latest recipes
our latest recipes
Herb Grilled Chicken Breast
Herb grilled chicken is a healthy choice for diabetics as it is Herb grilled chicken is a healthy choice for diabetics as it is …
Read MoreVideos List
Diet is an essential part of healthy living ,below you can find regional diet plan that can help you with your Lifestyle modification.









